A directory is a hierarchical structure that stores information about objects on the network. A directory, in the most generic sense, is a comprehensive listing of objects. A phone book is a type of directory that stores information about people, businesses, and government organizations. Phone books typically record names, addresses, and phone numbers.
Active Directory (AD) is a Microsoft technology used to manage computers and other devices on a network. It is a primary feature of Windows Server, an operating system that runs both local and Internet-based servers.
Benefits of Active Directory –
◉ Hierarchical organizational structure.
◉ Multimaster Authentication & Multimaster replication (the ability to access and modify AD DS from multiple points of administration)
◉ A single point of access to network resources.
◉ Ability to create trust relationships with external networks running previous versions of Active Directory and even Unix.
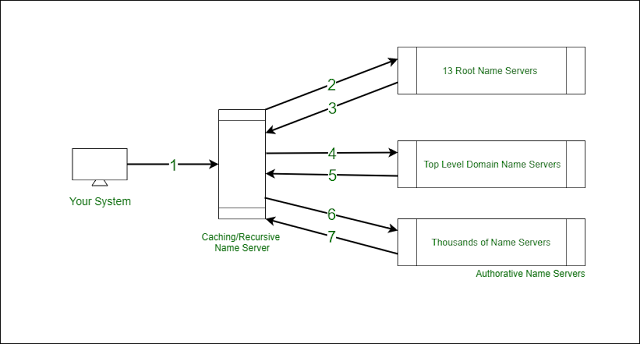
Directory Service –
A directory service is a hierarchical arrangement of objects which are structured in a way that makes access easy. However, functioning as a locator service is not AD’s exclusive purpose. It also helps organizations have a central administration over all the activities carried out in their networks. Essentially a Network Directory Service:
◉ Provides information about the user objects, computers and services in the network.
◉ Stores this information in a secure database and provides tools to manage and search the directory.
◉ Allows to manage the user accounts and resources, apply policies consistently as needed by an organization.
Active Directory provides several different services, which fall under the umbrella of “Active Directory Domain Services, ” or AD DS. These services include:
1. Domain Services –
Stores centralized data and manages communication between users and domains; includes login authentication and search functionality
2. Certificate Services –
It generates, manages and shares certificates. A certificate uses encryption to enable a user to exchange information over the internet securely with a public key.
3. Lightweight Directory Services –
Supports directory-enabled applications using the open (LDAP) protocol.
4. Directory Federation Services –
Provides single-sign-on (SSO) to authenticate a user in multiple web applications in a single session.
5. Rights Management –
It controls information rights and management. AD RMS encrypts content, such as email or Word documents, on a server to limit access.
Domain Controllers –
A server that is running AD DS is called a domain controller.Domain controllers host and replicate the directory service database inside the forest. The directory service also provides services for managing and authenticating resources in the forest.These servers host essential services in AD DS, including the following:
– Kerberos Key Distribution Center (kdc)
– NetLogon (Netlogon)
– Windows Time (W32time)
– Intersite Messaging (IsmServ)
Active Directory Objects:
1. Container Objects –
These objects can contain other objects inside them, and we can make collection from them. For Ex- Forest, Tree, Domains, Organisational Units.
2. Leaf Objects –
These objects can not contain other objects inside them. For Ex- users, computers, printers, etc.

Common Terminologies and Active Directory Concepts:
◉ Schema –
A set of rules, the schema, that defines the classes of objects and attributes contained in the directory, the constraints and limits on instances of these objects, and the format of their names.
◉ Global catalog –
A global catalog that contains information about every object in the directory. This allows users and administrators to find directory information regardless of which domain in the directory actually contains the data. For more information about the global catalog, see The role of the global catalog.
◉ Forest Root Domain –
The first domain that is installed in an Active Directory Forest is referred to as the root domain.
◉ Sites –
Sites in AD DS represent the physical structure, or topology, of your network. AD DS uses network topology information, which is stored in the directory as site, subnet, and site link objects, to build
the most efficient replication topology.
◉ Lightweight Directory Access Protocol –
AD is based on the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). This protocol provides a common language for clients and servers to speak to one another.