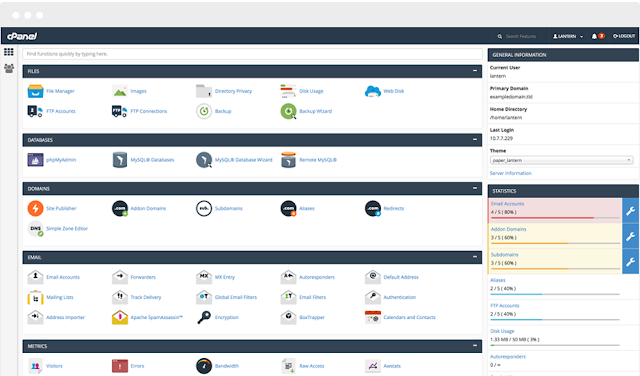
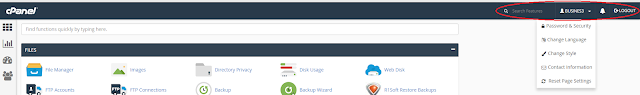
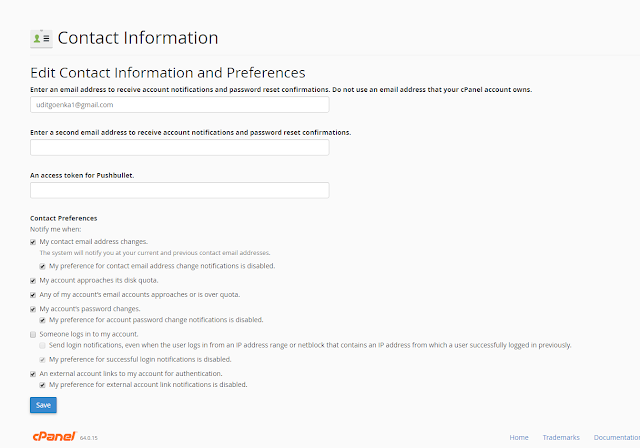
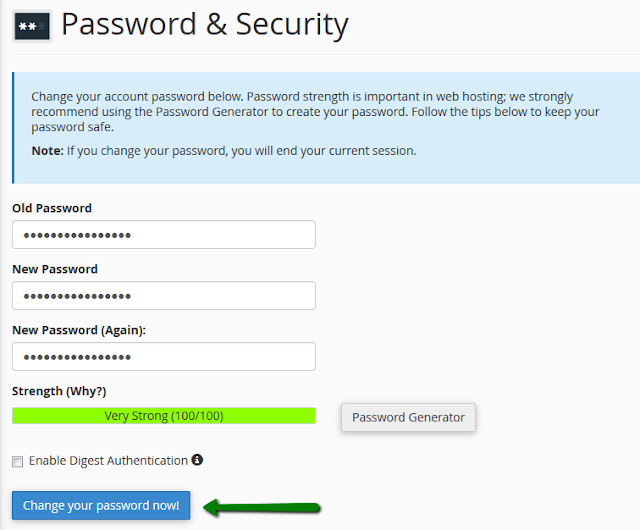
A DNS (Domain Name System) server, also known as a name server, is a web server that is specifically designed to connect with a massive database that stores all information about domain names and their corresponding DNS records. These records include the registrant of the domain, the web host, active nameservers and other information.
A domain name's DNS servers are listed in the WHOis database and the web hosting control panel, and appear as NS1.NAMESERVER.COM and NS2.NAMESERVER.COM.
There are thousands of DNS servers around the world that contain pieces of the database, but there are only 13 root DNS servers that contain the entire database on each server.
There are two types of DNS servers – primary and secondary. It is important to note, however, that any DNS server can be used as a primary or a secondary server, depending on the preference of the sever administrator. It is even possible to have the same server be a primary server for one zone and a secondary server for another.
If you're interested in learning more about primary and secondary DNS servers, then you may want to consider the following information.
A primary master name server reads data for the domain zone from a file located on the web server of the hosting account. This server usually also sends information to the secondary server as well.
Zone data is the information specified by the server administrator that tells the server how to behave and communicate with other servers. When a primary server communicates with a secondary server, it is called a zone transfer because zone data is being transferred from one DNS to another.
Two DNS servers are assigned to each domain to make administration easier and provide more security than just a single server. Once zone data has been created for a primary server, it does not need to be copied over to the secondary server because the two servers automatically share zone data.
A secondary DNS server, also called a slave server or simply a slave, receives zone data from the primary server automatically after starting. In Microsoft's DNS manager software, secondary DNS servers are referred to as secondaries. Every time a secondary server functions, it requests information from its master server.
It is important to note that a secondary server does not need to pull data form a primary server because another secondary server can be set up as the master server.
Secondary DNS servers are just as important as primary servers because they provide security in the form of redundancy. They also lessen the load placed on the primary server and ensure that there is always a server working to deliver data. By diversifying the administrative structure of domain name servers, the security of web sites and the internet in general is ensured.
A domain name's DNS servers are listed in the WHOis database and the web hosting control panel, and appear as NS1.NAMESERVER.COM and NS2.NAMESERVER.COM.
The Basics
There are thousands of DNS servers around the world that contain pieces of the database, but there are only 13 root DNS servers that contain the entire database on each server.
There are two types of DNS servers – primary and secondary. It is important to note, however, that any DNS server can be used as a primary or a secondary server, depending on the preference of the sever administrator. It is even possible to have the same server be a primary server for one zone and a secondary server for another.
If you're interested in learning more about primary and secondary DNS servers, then you may want to consider the following information.
Primary Master DNS Servers
A primary master name server reads data for the domain zone from a file located on the web server of the hosting account. This server usually also sends information to the secondary server as well.
Zone data is the information specified by the server administrator that tells the server how to behave and communicate with other servers. When a primary server communicates with a secondary server, it is called a zone transfer because zone data is being transferred from one DNS to another.
Two DNS servers are assigned to each domain to make administration easier and provide more security than just a single server. Once zone data has been created for a primary server, it does not need to be copied over to the secondary server because the two servers automatically share zone data.
Secondary DNS Servers
A secondary DNS server, also called a slave server or simply a slave, receives zone data from the primary server automatically after starting. In Microsoft's DNS manager software, secondary DNS servers are referred to as secondaries. Every time a secondary server functions, it requests information from its master server.
It is important to note that a secondary server does not need to pull data form a primary server because another secondary server can be set up as the master server.
Secondary DNS servers are just as important as primary servers because they provide security in the form of redundancy. They also lessen the load placed on the primary server and ensure that there is always a server working to deliver data. By diversifying the administrative structure of domain name servers, the security of web sites and the internet in general is ensured.